Electronics notice
Electronic tables and electronic calculations. Those values that are found here are not exactly accurate values, this is so accurate we could find it to be.
Ohms Law Calculators
Direct Current (DC)
Volt: U = R × I
Current: I = U ÷ R
Resistance: R = U ÷ I
Power: P = U × I
Alternative Current (AC)
Power: P = U × Z
Cross-sectional area of a cable
Cross-sectional Area: A = (I × L × K) ÷ (Ud × p
Voltage Divider Calculator
Voltage Divider Formula: UOUT = UIN × R2 ÷ (R1 + R2)
Voltage IN to Voltage Out Resistors Calculator: EXPERIMENTAL
100
[[ debug is enabled here ]]
LED Calculator
LED Resistance Formula: R1 = (Us - ULED) ÷ ILED
Resistor calculation
The Resistance is determen by a really simple way of colored rings that only is hard to see the actuall color because it is so small.
Printer friendly version of Resistor Colour Code Table
| Colour | Ring 1 | Ring 2 | Ring 3 | Ring 4 | Ring 5 | |||
| 4-Rings | 5-Rings | 4-Rings | 5-Rings | |||||
| First Digit | Second Digit | # of Zeros | Third Digit | Tolerance | # of Zeros | Tolerance | ||
| Black | - | 0 | None | 0 | - | None | - | |
| Brown | 1 | 1 | 1x | 1 | 1% | 1x | 1% | |
| Red | 2 | 2 | 2x | 2 | 2% | 2x | 2% | |
| Orange | 3 | 3 | 3x | 3 | - | 3x | - | |
| Yellow | 4 | 4 | 4x | 4 | - | 4x | - | |
| Green | 5 | 5 | 5x | 5 | - | 5x | - | |
| Blue | 6 | 6 | 6x | 6 | - | 6x | - | |
| Purple | 7 | 7 | 7x | 7 | - | 7x | - | |
| Grey | 8 | 8 | - | 8 | - | - | - | |
| White | 9 | 9 | - | 9 | - | - | - | |
| Silver | - | - | × 0.01 | - | 10% | × 0.01 | 10% | |
| Gold | - | - | × 0.1 | - | 5% | × 0.1 | 5% | |
There is however smaller resistors that are "Surface Mounted" (SMD) and thoose use digits and letters on the marking due to the tiny space available:
- Three-digit code markings. Example: 4R7 medium tolerance and this letter R is the decimal possition of the
4.7 Ωresistor. - Four-digit code markings. Example: 4702 high tolerance, the three first digit is the significant digit and the fourth is the multiplier.
470 × 102 = 47kΩ - EIA96 SMD resistor coding system. Example: 68X 1% tolerance
| Code | Significan Figure |
|---|---|
| 01 | 100 |
| 02 | 102 |
| 03 | 105 |
| 04 | 107 |
| 05 | 110 |
| 06 | 113 |
| 07 | 115 |
| 08 | 118 |
| 09 | 121 |
| 10 | 124 |
| 11 | 127 |
| 12 | 130 |
| 13 | 133 |
| 14 | 137 |
| 15 | 140 |
| 16 | 143 |
| 17 | 147 |
| 18 | 150 |
| 19 | 154 |
| 20 | 158 |
| 21 | 162 |
| 22 | 165 |
| 23 | 169 |
| 24 | 174 |
| Code | Significan Figure |
|---|---|
| 25 | 178 |
| 26 | 182 |
| 27 | 187 |
| 28 | 191 |
| 29 | 196 |
| 30 | 200 |
| 31 | 205 |
| 32 | 210 |
| 33 | 215 |
| 34 | 221 |
| 35 | 226 |
| 36 | 232 |
| 37 | 237 |
| 38 | 243 |
| 39 | 249 |
| 40 | 255 |
| 41 | 261 |
| 42 | 267 |
| 43 | 274 |
| 44 | 280 |
| 45 | 287 |
| 46 | 294 |
| 47 | 301 |
| 48 | 309 |
| Code | Significan Figure |
|---|---|
| 49 | 316 |
| 50 | 324 |
| 51 | 332 |
| 52 | 340 |
| 53 | 348 |
| 54 | 357 |
| 55 | 365 |
| 56 | 374 |
| 57 | 383 |
| 58 | 392 |
| 59 | 402 |
| 60 | 412 |
| 61 | 422 |
| 62 | 432 |
| 63 | 442 |
| 64 | 453 |
| 65 | 464 |
| 66 | 475 |
| 67 | 487 |
| 68 | 499 |
| 69 | 511 |
| 70 | 523 |
| 71 | 536 |
| 72 | 549 |
| Code | Significan Figure |
|---|---|
| 73 | 562 |
| 74 | 576 |
| 75 | 590 |
| 76 | 604 |
| 77 | 619 |
| 78 | 634 |
| 79 | 649 |
| 80 | 665 |
| 81 | 681 |
| 82 | 698 |
| 83 | 715 |
| 84 | 732 |
| 85 | 750 |
| 86 | 768 |
| 87 | 787 |
| 88 | 806 |
| 89 | 825 |
| 90 | 845 |
| 91 | 866 |
| 92 | 887 |
| 93 | 909 |
| 94 | 931 |
| 95 | 953 |
| 96 | 976 |
| Type | Ohms Law | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Current Resistance | U = I × R | P = U × I |
| One-phase Alternating Current Resistance | U = I × Z |
P = U × I × cos φ Q = U × I × sin φ S = U × I |
Capacitance
Charge: Q = I × t
Capacitance: C = Q × U
Capacitance: C = ε × A ÷ d
3-Digit Capacitor Calculator
| 1st Digit | 2nd Digit | 3rd Digit (Multiplier) |
|---|---|---|
| - | 0 | 0 / NONE |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 5 | 5 |
| 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 7 | 7 | 7 |
| 8 | 8 | 8 |
| 9 | 9 | 9 |
.
Some Capacitors are polarity sensitive!
Variable Capacitors are capacitors that can be changed.
Inductance
Under Construction
Impedance (Ω)
Z = √(R2 + XL2)
- Z = Impedance (Ω)
- R = Resistance (Ω)
- XL = Inductance Reactance (Ω)
Under Construction
Power
P = U * I
Solar Out
Power Output.
Material: Polycrystalline silicon Maximum power: 0.252-0.253 W Maximum current: 0.487 A Maximum voltage: 0.518 V Short-circuit current: 0.532 A Open circuit voltage: 0.564 V Conversion efficiency: 17.4% Size: L x W = 52 x 26mm Thickness: 0.25 mm Package Include: 100pcs 52*26mm solar panels
Solar-cells calculator
Solar-panel calculator
196.5354330732Mechanical & Hydraulic horsepower
1 hpI = 745.699872 W
Converter, Watt to Horsepower
Php = PW / 745.699872
1000 W (1 kW) = 1.34 hp (1.3410220888438 hp)
3.44 V × 1.5 A = 5.16W
Capacity = 20000mAh
Diodes
Diodes are polarized
Anodeis the Possitive shorted to A andCathodeshorted to C or K is the negative.Current flows in one direction but all diodes have a reverse bias that makes a tiny amount of electrons to flow trught in the wrong direction.
Transistors
A Transistor is a Semiconductor Device1 used to amplify and switch electronic signals and electrical power.
NPN vs PNP Transistors where N stands for Negative and P stands for Positive.
NPN - Negative-Positive-Negative.
PNP - Positive-Negative-Positive
| P-channel | |
|---|---|
| N-channel |
| Type | Description | Circuit |
|---|---|---|
| BC547 | NPN - I have done some logical circuits using this transistor: Tinker CAD, Auto Desk | |
| BC557 | PNP | |
| IRLZ44N | HEXFET power MOSFET | |
| IRF | HEXFET power MOSFET |
Thyristors
A Thyristor is two Semiconductor Devices1 connectied in such way so it switches only when the dirrection of voltage is changed.
Thyristors have both NPN and PNP doped and you can say it's like two Transistors one is NPN and the other one is PNP.
NPN - Negative-Positive-Negative.
PNP - Positive-Negative-Positive
Integrated Circuits (IC)
Integrated Circuit abbreviated as IC are often refered as a DIP and then followed with the total pins on it. For example: an IC with 4-pins on both sides are a DIP8 like the image bellow.
The content of an Integrated Circuit is a set of other components in nano scaled and connected as the schematic of the internal circuits.
IC - Integrated Circuit.
DIP# - Dual In-line Package Where # is replaced with the total set of pins.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| DIP8 | 2 pins × 4 rows set of pins. |
| DIP814 | 2 pins × 7 rows set of pins. |
| DIP816 | 2 pins × 8 rows set of pins. |
Common IC
A list of commonly used Integrated Circuits.
| IC Name | Name |
|---|---|
| 74HC595 (SN54HC595, SN74HC595) | 8-bit Shift Registers with 3-sate output registers |
| 555 (NA555, NE555, SA555, SE555) | Precision Timer |
SN74HC595N
NE555 - A-stable Online Calculator
RA: 10 kΩ
RB: 100 kΩ
C: 10 µF
Frequency ƒ: 14.553 Hz
0
1458333.3333333
1458333.3333333
| Result | Formula | |
|---|---|---|
| Output Duration tH | 0.693 × ( RA + RB ) × C × 1000 | |
| Output Duration tL | 0.693 × RB × C × 1000 | |
| Period |
0.693 × ( RA + ( 2 × RB ) ) × C × 1000
= tH + tL * 1000 |
|
| Frequency ƒ | 1.44 ÷ ( RA + ( 2 × RB ) ) × C | |
| Output Driver Duty Cycle ƒ | - |
RB ÷ ( RA + ( 2 × RB ) )
= tL ÷ ( tH + tL ) |
| Output Waveform Duty Cycle | - |
tH ÷ ( tH + tL )
= 1 - ( RB ÷ ( RA + ( 2 × RB ) ) ) |
| Low-to-High ratio | - |
tL ÷ tH
= RB ÷ ( RA + RB ) |
NE555 - Timer Integrated Circuits
Precision timer
NE555 "Astable" Circuit:
NE555 "Astable" Calculator:
THIGH Time period of high output
THIGH (ms) = 0.693 × (R1+R2) × C1 × 1000
TLOW (ms) = 0.693 × R2 × C1 × 1000
T (sec) = 0.693 × (R2 + 2 × R2) × C1
T (sec) = THIGH + TLOW
ƒ (Hz) = 1.44 ÷ (R1 + 2 × R2) × C1
PWT (%) = (T1/T)
THIGH- Time period of high (ON) signal in milliseconds.TLOW- Time period of low (OFF) signal in milliseconds.T- Time period sum of THIGH and TLOW in seconds.ƒ- The freqency of one cycle in Hertz.PWT- (Duty cycle) is the percentage ratio of the pulse duration/pulse width to the total of the period (T) in waveform. Represents time duration of the high signal.-
Example: R1 = 1kΩ R2 = 100kΩ C1 = 10µF
THIGH = 699.93 ms
TLOW = 693 ms
T = 1.39293 sec
ƒ = 7.1641791044776E-11 Hz
Frequency
Wavelenght is Distance divided by Cycles.
Frequency is Cycles divided by Time
The unit of measure used with rotating mechanical devices is revolutions per minute, abbreviated r/min or rpm. 60 rpm equals one hertz
- Hz - One cycle per second. 1 /
- RPM - Revolutions per minute
- PWM - Pulse-width modulation
- PDM - pulse-duration modulation
- MPPT - Maximum Power Point Tracking
7200 RPM = 120 Hz Hz = RPM / 60
5200 RPM = 86.666666666667 Hz Hz = RPM / 60
120 RPM = 2 Hz Hz = RPM / 60
60 RPM = 1 Hz Hz = RPM / 60
1 RPM = 0.016666666666667 Hz Hz = RPM / 60
120 Hz = 7200 RPM RPM = Hz * 60
90 Hz = 5400 RPM RPM = Hz * 60
60 Hz = 3600 RPM RPM = Hz * 60
30 Hz = 1800 RPM RPM = Hz * 60
1 Hz = 60 RPM RPM = Hz * 60
Frequency from Time or Period: ƒ = 1 ÷ T
Frequency from Wavelength: ƒ = V ÷ λ
λ = meter (m = nm × 1 m ÷ 109 nm)
Frequency of Electromagnetic Waves in a Vacuum: ƒ = C ÷ λ
C = Speed of Light = 3.00 x 108 m/s
I2C
I2C is a multi functional bus which means that multiple chips can be connected to the same bus pins.
The bus uses two pins for communications and one is a serial clock pin SCL and the other is a serial data pin SDA
Changing the I2C LCD address
Theese addresses apply to the most commonly used IC: PCF8574T that have switches or solderpads (A0, A1, A2) where 1 is no connection/ "switched off" and 0 is connected/ "switched on".
| A0 | A1 | A2 | HEX Address PCF8574T 1602 (16x2) |
HEX Address PCF8574T 2004 (20x4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | H | H | 0x27 | 0x3F |
| L | H | H | 0x26 | 0x3E |
| H | L | H | 0x25 | 0x3D |
| 0x24 | 0x3C | |||
| 0x23 | 0x3B | |||
| 0x22 | 0x3A | |||
| 0x21 | 0x39 | |||
| 0x20 | 0x38 |
| A0 | A1 | A2 | HEX Address |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0x27 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0x26 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0x25 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0x24 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0x23 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0x22 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0x21 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0x20 |
8 cm = 302.36220472441 px
3.5 cm = 132.28346456693 px
Logic Gates & Latches
Logic Gates are the base inputs to create electronic circuits.
A Logic Gate in electronics is an physical device that implement some rules and are defined by an Boolean algebra.
Logic Gates are input to output in diffrent stages similar to the Conditions: if(){} , else if(){} , else{} and Booleans: TRUE or FALSE used in memory/storage, programming and electronics.
| Basic | Inverted | Exclusive | Inverted Exclusive | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BUFFER | OR | AND | NOT | NOR | NAND | XOR | XAND | XNOR | XNAND |
| Flip-Flop Latch (Memory) | Implement | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR-NAND | SR-NOR | SR-AND-OR | D | T | JK | IMPLY |
| Name | Description | Symbol | Truth table | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BUFFER-Gate |
A basic logic gate that passes its input (unchanged) to its output. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Boolean Algebra:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| OR-Gate |
Takes two inputs and returns the output if one or both input(s) is true. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Boolean Algebra:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| AND-Gate |
Takes two inputs and returns the output if both inputs are true. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Boolean Algebra:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Name | Description | Symbol | Truth table | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOT-Gate | A basic logic gate that passes its input (inverted) to its output. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Boolean Algebra: |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| NOR-Gate | Takes two inputs and returns the output if both inputs are false. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Boolean Algebra: |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| NAND-Gate | Takes two inputs and returns the output if both inputs are true. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Boolean Algebra: |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Name | Description | Schematic Symbol | Truth table | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XOR-Gate | Takes two inputs and returns the output if both input is true but not if both inputs are true... |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Boolean Algebra: |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Name | Description | Schematic Symbol | Truth table | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XNOR-Gate | Takes two inputs and returns the output if both inputs are true or false. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Boolean Algebra: |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Name | Description | Schematic Symbol | Truth table | SR-NAND | Takes two inputs and converts it to a memory/storage. The set (S) input sets the output TRUE state and the reset (R) returns the output FALSE. The input is Logic 0 witch means it is set by a ground signal. |
|
|---|---|---|---|
- RTL Resistor-Transistor Logic
- is a class of digital circuits built using resistors as the input network and bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) as switching devices.
- DTL Diode-Transistor Logic
- TTL Transistor-Transistor Logic
- FET Field-Effect Transistor
- CMOS Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor
Test
More than one/two input on gates?
Yes, there can be more than the designated inputs. For three gates this gates appear like this:
OR-Gate
| A | B | C | A OR B OR C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
NOR-Gate
| A | B | C | A NOR B NOR C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
AND-Gate
| A | B | C | A AND B AND C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
NAND-Gate
| A | B | C | A NAND B NAND C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
Can a buffer gate have more than one input?
No, because it then needs one or more outputs to be quallified as a multi-gate buffer. It only can have two or more buffers separated like this: A == C, B == D.
Actually yes, but it becomes a set of gates to make it happen. Let's figure out the gates to use:EXPERIMENTAL STATEMENT
A, B == C?
(XOR + OR + AND) AND == ?
- (A XOR B = Q0) +
- (A OR B = Q1) +
- (A AND B = Q2) =
- Q1 AND Q2 AND Q3 = Q
Where A and B are in parallel and outputs are constrained into a three-input AND-Gate:
| A | B | Q |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | |
| 0 | 1 | |
| 1 | 0 | |
| 1 | 1 |
XOR
| A | B | A XOR B |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
OR
AND
Step Motor
A step motor can you find in old scanners and printers and also in 3D Printers and CNC Machines.
BI-polar step motors are four wired with two coils.
UNI-polar step morors are six wired with two coils that have a seperated coil center connected wire for each coils.
Hybrid step motors are often five wired with two coils that have a common coil center connected wire.
H-Bridge
Stepmotors use a simple "H-Bridge" for each coil. Most common is the 4-pin stepmotors.
A simple H-Bridge uses two N-Channel and two P-Channel MOSFET's.
There is a way to use four N-Channel MOSFET's but you need to ensure the upper-side of the two MOSFET's do turn on fully, otherwise you have plenty of heat depending on your load
Unconfirmed solution, may or may not work:
To fully turn on the two upper-side MOSFET's you need to get the gate's voltage higher than the source and drain voltage.
IMAGE BELLOW DOES NOT ILLUSTRATE A FUCTIONAL H-BRIDGE.
18650 Battery
This types of batteries can be found mostly in old laptops battery packs, just look for the Li-ion badge if you plan to recycle them!
Power Wall & Solar Power Banks DIY
You can create your own Power Wall! You only need to get a lot of old laptop batteries with the Li-ion badge and take the form-faktor in concideration because the size of battery packs does matter!
Battery Pack Calculator Table
Batteries in Series creates higher Voltage (U:V) and batteries in Parallel creates more Ampere (I:mA or I:A).
3.7V, 3000mAh, 12 series, 8 parallel
| Cell | Total Cells | Series | Parallel | VNOM | EXPERIMENTALAMAX (Load) |
EXPERIMENTALkWMAX (Load) |
Ah (Battery capacity) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (18650) 3.7 V @ 2200 mAh | 130 | 13 | 10 | 48.1 V | 20.8 A | 1 kW | 22 Ah (22000 mAh) |
| (18650) 3.7 V @ 4400 mAh | 130 | 13 | 10 | 48.1 V | 20.8 A | 1 kW | 44 Ah (44000 mAh) |
Other types of Li-ion (Lithium-ion) batteries
Where the 18650-type battery type is the most commonly used in old laptop batteries, electric cars and E-wape's etc.
| Type | MIN capacity | MAX capacity |
|---|---|---|
| 14 400 | 600 mAh | 700 mAh |
| 14 430 | 500 mAh | 600 mAh |
| 14 500 | 700 mAh | 800 mAh |
| 14 650 | 900 mAh | 1000 mAh |
| 16 650 | 2100 mAh | 2500 mAh |
| 18 500 | 1300 mAh | 1900 mAh |
| 18 650 | 2000 mAh | 3500 mAh |
| 20 700 | 3000 mAh | - mAh |
| 14 400 | 14 430 | 14 500 | 14 650 | 16 650 | 18 500 | 18 650 | 20 700 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAX Capacity | 700 mAh | 600 mAh | 800 mAh | 1000 mAh | 2500 mAh | 1900 mAh | 3500 mAh | - |
| MIN Capacity | 600 mAh | 500 mAh | 700 mAh | 900 mAh | 2100 mAh | 1300 mAh | 2000 mAh | 3000 mAh |
LCD character set table
LCD character is 5×7=35 Pixels in size.
Some random calculations:
- LCD-1602 (16 col × 2 rows) have
( ( 5 × 7 ) × 16 ) × 2 = 1120 pixelsin total. - LCD-2004 (20 col × 4 rows) have
( ( 5 × 7 ) × 20 ) × 4 = 2800 pixelsin total.
Applies to chip: HD44780U with ROM code: A00
| Lower 4 bits |
Upper 4 bits | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
00x0#0000 |
10x1#0001 |
20x2#0010 |
30x3#0011 |
40x4#0100 |
50x5#0101 |
60x6#0110 |
70x7#0111 |
80x8#1000 |
90x9#1001 |
A0xA#1010 |
B0xB#1011 |
C0xC#1100 |
D0xD#1101 |
E0xE#1110 |
F0xF#1111 |
|
00x#00000 |
CG RAM (char)0 0x00 |
0x10 |
0x20 |
0x30
|
0x40
|
0x50
|
0x60
|
0x70
|
0x80 |
0x90 |
0xA0 |
0xB0
|
0xC0
|
0xD0
|
0xE0
|
0xF0
|
10001 |
CG RAM(char)1 |
|||||||||||||||
20010 |
CG RAM(char)2 |
|||||||||||||||
30011 |
CG RAM(char)3 |
|||||||||||||||
40100 |
CG RAM(char)4 |
|||||||||||||||
50101 |
CG RAM(char)5 |
|||||||||||||||
60110 |
CG RAM(char)6 |
|||||||||||||||
70111 |
CG RAM(char)7 |
|||||||||||||||
81000 |
||||||||||||||||
91001 |
||||||||||||||||
A1010 |
||||||||||||||||
B1011 |
||||||||||||||||
C1100 |
||||||||||||||||
D1101 |
||||||||||||||||
E1110 |
||||||||||||||||
F1111 |
||||||||||||||||
Display custom character
Don't find what you like to print on the display in one character?
There is a way to make up to 7-custom characters and save them to the I2C-chip by using the following lines of code:
You need to download the "LiquidCrystal_I2C" library and change the I2C-address and then set the type of display.
Istalling the library by using the Arduin IDE's tool bar as following: Sketch > Include library > Manage libraries then filter your search: LiquidCrystal I2C
lcd1(I2C-address,cols,rows)ff7f0
/******************************************************************************* * @author Jesper 'TXM-MC' Johansson * @project Arduino * @file Custom_I2C_Character.ino * @created 10 Apr 2018 23:33:41 * @copyright 2018 * * All rights reserved. * Distribution of the software in any form is only allowed with * explicit, prior permission from the owner. * * https://TXM-MC.homeserver.com/Arduino/Custom_I2C_Character/Custom_I2C_Character.ino/ ******************************************************************************/ #include <LiquidCrystal_I2C.h> LiquidCrystal_I2C lcd1(0x27,16,2); // This defines "lcd1" with the connected display with "I2C-address,cols,rows" so it knows where to display it! uint8_t celsius[8] = {0x08,0x14,0x08,0x03,0x04,0x04,0x03}; void setup(){ // Serial.begin(9600); // Serial monitor is not required for this! =) lcd1.init(); lcd1.backlight(); lcd1.createChar(0, celsius); // This creates the custom character. } void loop(){ lcd1.setCursor(0,0); lcd1.print("Celsius: "); lcd1.print((char)0); lcd1.print("=) "); delay(500); }
| Display Apperance | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 | HEX | DEC | BIN |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0x00 | 0 | B00000 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0x01 | 1 | B00001 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0x02 | 2 | B00010 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0x03 | 3 | B00011 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0x04 | 4 | B00100 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0x05 | 5 | B00101 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0x06 | 6 | B00110 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0x07 | 7 | B00111 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0x08 | 8 | B01000 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0x09 | 9 | B01001 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0x0A | 10 | B01010 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0x0B | 11 | B01011 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0x0C | 12 | B01100 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0x0D | 13 | B01101 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0x0E | 14 | B01110 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0x0F | 15 | B01111 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0x10 | 16 | B10000 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0x11 | 17 | B10001 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0x12 | 18 | B10010 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0x13 | 19 | B10011 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0x14 | 20 | B10100 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0x15 | 21 | B10101 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0x16 | 22 | B10110 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0x17 | 23 | B10111 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0x18 | 24 | B11000 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0x19 | 25 | B11001 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0x1A | 26 | B11010 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0x1B | 27 | B11011 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0x1C | 28 | B11100 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0x1D | 29 | B11101 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0x1E | 30 | B11110 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0x1F | 31 | B11111 |
Celsius symbol:
uint8_t celsius[8] = {0x08,0x14,0x08,0x03,0x04,0x04,0x03};
| 0x08 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x14 | |||||
| 0x08 | |||||
| 0x03 | |||||
| 0x04 | |||||
| 0x04 | |||||
| 0x03 |
Fahrenheit symbol:
uint8_t fahrenheit[8] = {0x08,0x14,0x08,0x07,0x04,0x06,0x04};
| 0x08 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x14 | |||||
| 0x08 | |||||
| 0x07 | |||||
| 0x04 | |||||
| 0x06 | |||||
| 0x04 |
Kelvin symbol:
uint8_t kelvin[8] = {0x08,0x14,0x08,0x05,0x06,0x05,0x05};
| 0x08 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x14 | |||||
| 0x08 | |||||
| 0x05 | |||||
| 0x06 | |||||
| 0x05 | |||||
| 0x05 |
Ohmega (Ohm) symbol:
uint8_t ohmega[8] = {0x00,0x0E,0x11,0x11,0x11,0x0A,0x1B};
| 0x00 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x0E | |||||
| 0x11 | |||||
| 0x11 | |||||
| 0x11 | |||||
| 0x0A | |||||
| 0x1B |
byte ohmega[8] = {B00000,
B01110,
B10001,
B10001,
B10001,
B01010,
B11011,
B00000,
};
Gear Ratio
- AIN - Input Gear
- BOUT -
"Gear-to-Gear" (G2G)
Low-speed, High-Tourque
High-speed, Low-Tourque
TCP Header (TCP-IP)
The Internet protocol suite is the conceptual model and set of communications protocols used on the Internet and similar computer networks.
It is commonly known as TCP/IP because the foundational protocols in the suite are the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Internet Protocol (IP).
It is occasionally known as the Department of Defense (DoD) model because the development of the networking method was funded by the United States Department of Defense through DARPA.
The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is one of the main protocols of the Internet protocol suite.
| Bit | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Byte | Version (4-bits) |
IHL (4-bits) |
Type of Service (TOS) (8-bits) |
Total Length (16-bits) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Byte | Identification (Fragment ID) (16-bits) |
D F |
M F |
Fragment offset (13-bits) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Byte | Time-To-Live (TTL) (8-bits) |
Protocol (8-bits) |
Header Checksum (16-bits) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Byte | Source Address (32-bits) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Byte | Destination Address (32-bits) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Byte | Options (If any, variable length, padded with zero's, 40 bytes max length) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Byte | Options (If any, variable length, padded with zero's, 40 bytes max length) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Byte | Options (If any, variable length, padded with zero's, 40 bytes max length) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Byte | Options (If any, variable length, padded with zero's, 40 bytes max length) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Byte | Options (If any, variable length, padded with zero's, 40 bytes max length) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
RJ45 (Ethernet)
EIA/TIA T568B Straight-Through pin layout
| Pin | 568A Standard | 568B Standard | 10/100 BASE-T (10/100 Mbps) |
1000 BASE-T (1 Gbps) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | █████ Green/White | █████ Orange/White | Tx+ | BI_DA+ |
| 2 | █████ Green | █████ Orange | Tx- | BI_DA- |
| 3 | █████ Orange/White | █████ Green/White | Rx+ | BI_DB+ |
| 4 | █████ Blue | █████ Blue | N/C | BI_DC+ |
| 5 | █████ Blue/White | █████ Blue/White | N/C | BI_DC- |
| 6 | █████ Orange | █████ Green | Rx- | BI_DB- |
| 7 | █████ Brown/White | █████ Brown/White | N/C | BI_DD+ |
| 8 | █████ Brown | █████ Brown | N/C | BI_D- |
Electric Power Consumption Calculator
Based on Swedish electric company (Vattenfall) taxies and prices.
Using region: South Area (S-region), Price teriff: E4 Price Plan (Type of connection): 16A.
Using region: North Area (N-region), Price teriff: T4 Price Plan (Type of connection): Appartment.
Consumption: 80 kWh.
Total price: 406 SEK
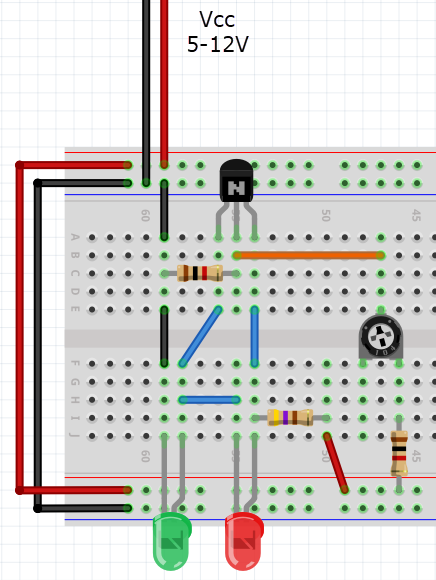
Usefull Circuits
A simple use with simple circuits!
9V Battery low indicator
Parts used:
- 2× LED's (Red & Green).
- 1× 1kΩ potentiometer.
- 2× 1kΩ resistors.
- 1× 470Ω resistor.
- 1× BC547 transistor.
- 1× breadboard.
- Some breadboard/jumper wires.
Arduino
Pin Layouts for Arduino UNO, Arduino MEGA 2560, Arduino NANO & Arduino Pro MINI
Raspberry PI
Pin Layouts for Raspberry PI B+ & Raspberry PI 3 B+
Formulas
Name Abbreviations
Under T Construction
Ω
Electronics (NEW, Orginized, comming soon!)
Tasks
Pi
Electronics
Resistors
A Resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component1 that act to reduce current flow and at the same time act to lower voltage levels within circuits.
Resistors Colour Code Table
Resistors can look so different because there is Resistors that are soldered on surface and those there goes thrum the circuit board.
The table bellow is for those resistors that goes thrum the circuit board and that have four or five "colour rings" on.
| Colour | Ring 1 | Ring 2 | Ring 3 | Ring 4 | Ring 5 | |||
| 4-Rings | 5-Rings | 4-Rings | 5-Rings | |||||
| First Digit | Second Digit | # of Zeros | Third Digit | Tolerance | # of Zeros | Tolerance | ||
| Black | - | 0 | None | 0 | - | None | - | |
| Brown | 1 | 1 | 1x | 1 | 1% | 1x | 1% | |
| Red | 2 | 2 | 2x | 2 | 2% | 2x | 2% | |
| Orange | 3 | 3 | 3x | 3 | - | 3x | - | |
| Yellow | 4 | 4 | 4x | 4 | - | 4x | - | |
| Green | 5 | 5 | 5x | 5 | - | 5x | - | |
| Blue | 6 | 6 | 6x | 6 | - | 6x | - | |
| Purple | 7 | 7 | 7x | 7 | - | 7x | - | |
| Grey | 8 | 8 | - | 8 | - | - | - | |
| White | 9 | 9 | - | 9 | - | - | - | |
| Silver | - | - | × 0.01 | - | 10% | × 0.01 | 10% | |
| Gold | - | - | × 0.1 | - | 5% | × 0.1 | 5% | |
This Resistor calculator/viewer is under constructions so be aware of that it can display the wrong value! The "E12-Serie" is the comonly used serie of pre-defined resistance value. Please double check before applying the resistor to a circuit or to a project here!
| Type | Ohms Law | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Current Resistance | U = I × R | P = U × I |
| One-phase Alternating Current Resistance | U = I × Z | P = U × I × cos φ Q = U × I × sin φ S = U × I |
| Type | Voltage | Resistance | Current | Effect | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serial Resistance | U = U1 + U2 + U3 + U++ | R = R1 + R2 + R3 + R++ | ||||||||||||||||
| Parallel Resistance | I = I1 + I2 + I3 + I++
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Three-phase Alternating Current Resistance (Y-Connection) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Three-phase Alternating Current Resistance (D-Connection) |
Transistors
A Transistor is a Semiconductor Device1 used to amplify and switch electronic signals and electrical power.
NPN vs PNP Transistors where N stands for Negative and P stands for Positive.
NPN - Negative-Positive-Negative.
PNP - Positive-Negative-Positive
Capacitors
A Capacitor is a Passive two-terminal electrical component1 used to store electrical energy temporarily in an electronic field.
Ceramic Capacitors are often flat, round and are commonly coloured █ brown-orange
Some Capacitors are polarity sensitive!
Variable Capacitors are capacitors that can be changed.
Calculation Table
| Third Digit | Multiplier | Letter | Tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | D | 0.5 pF |
| 1 | 10 | F | 1 % |
| 2 | 100 | G | 2 % |
| 3 | 1 000 | H | 3 % |
| 4 | 10 000 | J | 5 % |
| 5 | 100 000 | K | 10 % |
| 6, 7 | Not Used | M | 20 % |
| 8 | .01 | P | + 100, -0% |
| 9 | .1 | Z | +80, -20% |
Inductors
An Inductor is a passive two-terminal electrical component1 which resist changes in electric current passing through.
Diodes
A Diode is a two-terminal electronic component1 that conducts primarily in one direction.
Formulas
| Direct Current (DC) | Single-phase Alternating Current (AC) | Three-phase Alternating Current (AC) |
Ohms Law (DC)U = I × R Effect (DC)P = U × I |
Ohms Law (AC)U = I × Z Effect (AC)P = U × I × cos φ Q = U × I × sin φ S = U × I |
LED
SI-System Base units
| Magnitude | Unit | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Designation | Name | Designation | DC | AC |
| Voltage | U | Voltage | V |
U = I × R |
|
| Current | I | Ampere | A | ||
| Resistance | R | Ohm | Ω | ||
| Power | P | Watt | W | ||
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ||
Electronic SI Units Table
| Unit | Identifier | Name | Identifier | Equation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U | Voltage | V | I × R = U | ||||
| Current | I | Ampere | A |
|
Raspberry Pi Clock
1.3cm x 2cm